Learn all you need to know about the accounts receivable aging report, why it is important, and how to prepare it.
You need an accounts receivable aging report to help structure a workable company operating budget. It shows you the balance clients owe you against the duration outstanding broken down into categories. The report allows you to identify invoices still open, help follow up with your customers, and analyze their financial reliability to improve your bad credit risk awareness.
We've created this guide to help you better understand the accounts receivable aging report. We'll go over what this report is, why it's important, what it contains, and how to prepare it.

What is an aging report?
An aging report (or an accounts receivable aging report) refers to a record of overdue invoices, accounts receivable, or unused credit memos by periodic date changes. Businesses use aging reports to determine which customers have outstanding invoice balances.
As a collection tool, an aging report makes it easy for business owners and senior management to identify late-paying customers or bad debts, and analyze how their collection processes are faring. Thus, given its use as a collection tool, you could configure your reports to contain the contact information for each customer to make it easier to follow up with them.
Typically, accounts receivable aging reports contain invoices. However, as stated earlier, they can also include credit memos customers have not used. Credit memos are accounts payable and refer to transactions posted on customers' invoices to serve as a payment or reduction.
Why an AR aging report is important
Accounts receivables (AR) aging reports help businesses track their outstanding payments from customers. Companies want to sell products and services, and receive timely payments. Hence, they must always keep track of their finances and stay on top of who owes them to maintain their financial health.
1. Stay on top of your billings
AR aging reports show you customers who repeatedly fail to pay their invoices. You can then contact them to follow up on the invoice, allowing you to stay ahead of your billing and collection processes. Regular follow-up prevents late payments and reduces bad debt occurrences.
2. Sever ties with your clients
Aging reports show you which clients to sever ties with to prevent losses. For example, you can let go of clients who continually fail or struggle to pay their invoices.
3. Maintain healthy cash flow
Late payments are problematic for several reasons, including disrupting a company's cash flow. A healthy cash flow through your business is essential in running a successful enterprise. Companies can fail when customers stop paying. However, a lot more businesses fail because of mismanaged cash flows.
An aging report allows you to identify problems and issues in accounts receivable. You can then take steps to remedy those problems, such as getting clients to pay invoices faster or preventing cash flow issues.
4. Identify bad credit risks
The AR aging report method can help you estimate your uncollectible debts, including the approximate amount of receivables you may not collect for one reason or another. You can then use this as the end balance of allowance for your doubtful accounts.
Often, the longer accounts receivables remain outstanding, the less likely you will collect them. You're left with adjusted general journal entries for bad debt expense, which you can later use to identify bad credit risks early and avoid them.
5. Alter your credit policies
AR aging reports help identify customers behind on payments. As you go through the report, you may notice one or two clients responsible for most of your late payments and proceed with the necessary measures. However, if you note multiple clients with repeated late payments, it indicates a credit policy issue.
In such cases, you should compare your credit risk and policy to industry standards to see if you take too much risk or need to make adjustments.
6. Improve your collection process
AR aging reports allow you to analyze your collection process. For example, numerous old accounts receivable, mostly clocking over 60 or 90 days, indicate you may have a weak collection process. Thus, if you notice this trend from your reports, you can remedy the situation by adjusting your collection practices, sending invoices correctly, or hiring a debt collection agency.
What is included in an accounts receivable aging report?
The AR aging report lists each of your client's outstanding balances. It sorts the invoice balances into columns as follows:
- Current (Invoices due immediately)
- 1 to 30 days past due
- 31 to 60 days past due
- 61 to 90 days past due
- Over 120 days past due
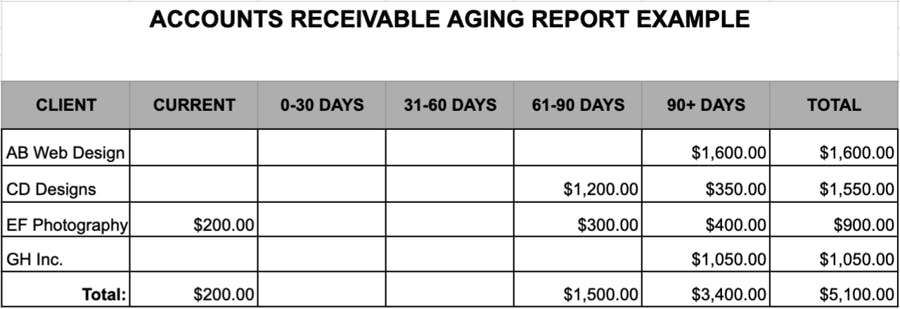
Below is an example of an AR aging report as of December 31, 2021:
4 steps to prepare accounts receivable aging report
When preparing an AR aging report, you require your customers' names, outstanding balance amounts, and aging schedules. The aging schedule table shows the relationship between your unpaid invoices and business bills with their respective due dates. To prepare it, you break down the accounts receivables into age categories and indicate against the names the total outstanding balances for specified periods.
1. Review open invoices
Start with reviewing all your outstanding invoices to get a complete look at things at the report's end.
2. Categorize customers according to the aging schedule
Next, sort all invoices by customer name and itemize each client's invoice. Sort them out by invoice date or number.
3. Create a list of customers with outstanding invoices
Then, create a list of your clients with outstanding invoice balances. You will include these clients in your final AR aging report.
4. List customers according to the number of days outstanding
Finally, list the clients on your AR aging report according to the number of days due on their invoices. You can reconfigure your report for different data ranges if you generate your report using an accounting software system.
Your AR aging report could also contain credit memos that customers have yet to use or which you have not matched against unpaid invoices.
Aging report FAQs
Why is an accounts receivable aging report needed for an audit?
Your company's auditors may use the accounts receivables aging report to select invoices and accounts they want to issue confirmations during their annual audit process.
What does an aging report show?
An AR aging report provides information about certain receivables based on invoice ages. It gives your management or billing and collection teams a historical overview of the business' receivables portfolio. Additionally, It groups outstanding invoices in categories of periods they have remained due or unpaid.
What is the aging schedule?
The aging schedule table shows the relationship between your unpaid invoices and business bills with their respective due dates. To prepare it, you break down the accounts receivables into age categories and indicate against the names the total outstanding balances for specified periods. It lists accounts receivables as
- Current
- less than 30, 60, and 90 days old
- Over 90 days
What is an accounts payable aging report?
It is a summary report detailing the balances you owe others. It helps you organize, visualize, and account for the amounts you owe. Typically, an accounts payable aging report includes vendor names and how much money you owe, each arranged in time buckets to help you determine overdue invoices for payment.




